
AI in Email Marketing- Smarter, Faster, and More Personal
February 24, 2025
Email List Segmentation- Tips for Better Email Marketing
March 3, 2025SMTP Protocol is a basic system for sending emails. It helps move emails from one server to another so they reach the right person. This system was made in the 1980s and is still used today. Since emails are very common, it is important to know how the SMTP Protocol works. Developers, network managers, and businesses that send many emails need to understand it. SMTP Protocol ensures emails are sent quickly and correctly.

In this blog, we will explore how it works, its importance, and how businesses optimize it for secure email delivery.
Table of Contents
How SMTP Protocol Works
Sure! Here’s a simple and expanded explanation of how the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) works to send emails.
Step 1: Writing the Email
First, you open your email app, like Gmail or Outlook, and write a message. You enter the recipient’s email address, type your message, and click Send.
Step 2: Connecting to the Mail Server
Once you press send, your email app connects to a mail server. This is a special computer that helps send emails. It uses a system called SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) to do this job.
Step 3: Verifying the Sender
Sometimes, the mail server checks if you are allowed to send emails. This is called authentication. You may need to enter your email username and password to prove that you are a real user.
Step 4: Sending the Email
After verification, the mail server takes your email and finds the recipient’s mail server. It sends your message over the Internet, like how a post office sends a letter.
Step 5: Delivering the Email
The recipient’s mail server receives the email and stores it safely. When the person opens their email app, the mail server delivers the email to their inbox.
Pricing
| Trail Plan | Standard Plan | Premium Plan | Professional Plan |
| $50 | $145 | $185 | $225 |
| Sending Limit | Sending Limit | Sending Limit | Sending Limit |
| 1000 Emails/Hour | 1500 Emails/Hour | 3000 Emails/Hour | 5000 Emails/Hour |
SMTP Protocol Example
Let’s say a user named User1 with the email [email protected] wants to send an email to User2 at [email protected].
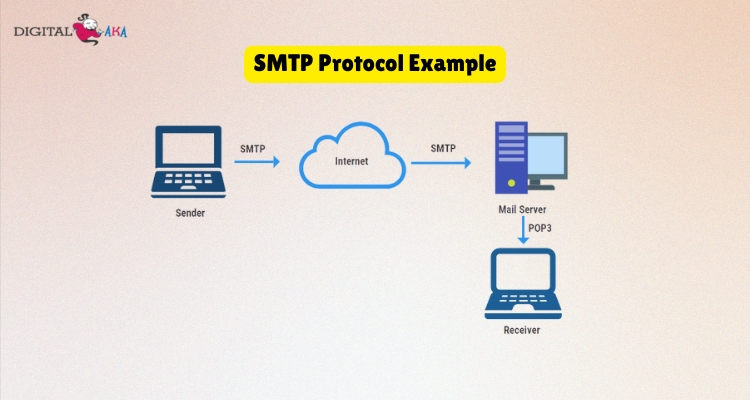
Step 1: Composing and Sending the Email
- User1 writes an email using an email client like Outlook, Gmail, or Thunderbird. When they hit “Send,” the client starts sending the email using the SMTP protocol.
Step 2: Connecting to the Sender’s Mail Server
- The email client connects to the sender’s mail server, which is smtp.123.com. This mail server is responsible for sending the email to the correct destination.
Step 3: Forwarding the Email to the Recipient’s Mail Server
- The sender’s mail server looks at the email address [email protected] and determines where to send it. It then finds the recipient’s mail server, smtp.recipient.com.
- Using the SMTP server protocol, the sender’s mail server forwards the email to the recipient’s mail server.
Step 4: Storing the Email on the Recipient’s Mail Server
- Once the email reaches smtp.recipient.com, it is stored in User2’s mailbox on the mail server.
Step 5: Retrieving the Email
- User 2 can now open their email client (e.g., Gmail or Outlook) and check their inbox. Their email client will use a retrieval protocol like IMAP or POP3 to fetch the email from the mail server.
Final Step: Reading the Email
- Now, User2 can open and read the email sent by User1. The process is complete!
- This is how SMTP helps in sending emails between two users.
SMTP Protocol Auth and Security Mechanisms
To protect email communication, SMTP uses authentication methods to make sure only authorized users can send emails.
Here are the three most common authentication methods:
1. Plain Authentication (Basic Username and Password Verification)
This is the simplest method. When you send an email, you enter a username (usually your email address) and a password. The email server checks if the information is correct. If it matches, you are allowed to send emails. However, this method is not very safe because hackers can steal the username and password if the connection is not secure.
2. STARTTLS Encryption (Securing the Connection)
STARTTLS is a security feature that encrypts the connection between your device and the email server. This means that even if someone tries to intercept your email, they will see only scrambled data, not your actual message. This method makes email communication much safer than plain authentication.
3. OAuth Authentication (Using Tokens Instead of Passwords)
OAuth is a modern and highly secure method. Instead of using a password, you log in through a trusted service (like Google or Microsoft). The service then gives a unique token to verify your identity. This way, your password is never shared directly, reducing the risk of hacking.
Email Protocol SMTP vs Other Email Protocols
There are three main email protocols:
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) – Used for sending emails.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) – Used for receiving emails on one device.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) – Used for receiving emails on multiple devices.
1. SMTP – Sending Emails
- SMTP is like a postman who delivers your email to the recipient.
- It works when you press “Send” on an email.
- SMTP servers take the email and transfer it to the recipient’s email server.
- It does not store emails permanently; it only helps in sending them.
Example:
- When you send an email from Gmail, Yahoo, or Outlook, SMTP carries the message to the receiver’s email provider.
2. POP3 – Receiving Emails on One Device
- POP3 is like a mailbox where you collect letters, but once you take them out, they are removed from the mailbox.
- It downloads emails from the server to your device (computer, phone, etc.) and deletes them from the server.
- You can read emails offline, but you cannot access them from another device.
- Best for users who prefer storing emails on a single device.
Example:
- If you check your email on your laptop using POP3, it will be downloaded to the laptop and deleted from the server. You won’t see the email on your phone later.
3. IMAP – Receiving Emails on Multiple Devices
- IMAP is like a cloud-based mailbox where emails stay on the server.
- You can access emails from multiple devices (computer, phone, tablet).
- It allows synchronization, meaning changes (like deleting or reading an email) appear on all devices.
- Best for users who want to access emails from different locations.
Example:
- If you check your email on your phone using IMAP, the email remains on the server. Later, you can see the same email on your laptop.
Protocol for SMTP: Technical Aspects
Here are the key aspects of SMTP in simple terms:

1. Port Numbers (How SMTP Connects)
SMTP uses special doorways called “ports” to send emails between servers. The most common ports are:
- Port 25 – Used for sending emails between mail servers.
- Port 465 – A secure port that encrypts emails for safe delivery.
- Port 587 – Used for sending emails from an email app (like Outlook or Gmail) to the server.
2. Important SMTP Commands (How Servers Communicate)
SMTP servers use short instructions called “commands” to send emails. Some important commands are:
- HELO (or EHLO) – Introduces the email sender to the receiving server.
- MAIL FROM – Tells the server who is sending the email.
- RCPT TO – Tells the server who should receive the email.
- DATA – Sends the actual message content (email text and attachments).
3. SMTP Response Codes (How Errors Are Shown)
After sending an email, SMTP servers give response codes to show if the email was delivered successfully or if there was a problem. Common codes include:
- 250 – Success! The email was accepted.
- 550 – Error! The recipient’s mailbox is unavailable (maybe the email address is wrong)
Advantages and Disadvantages of SMTP Protocol
Below are its advantages and disadvantages explained readily.
Advantages of SMTP Protocol
1. Reliable Email Delivery
- SMTP ensures that emails are sent successfully to the recipient.
- If an email cannot be delivered immediately, the server tries again.
- This makes email communication more dependable.
2. Scalability (Works for Small and Big Systems)
- SMTP can handle a small number of emails or millions of emails.
- It is used by individuals, businesses, and large organizations without problems.
- This makes it suitable for both personal and professional use.
3. Standardized and Universally Used
- SMTP is a common standard that all email services follow.
- Because of this, different email providers (like DigitalAka, Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook) can send and receive emails without issues.
- This makes email communication smooth across the world.
4. Resend Emails If Delivery Fails
- If the recipient’s server is down or busy, SMTP stores the email and tries sending it again later.
- This increases the chances of successful email delivery.
5. Supports Multiple Devices and Applications
- SMTP works with computers, mobile phones, tablets, and other smart devices.
- It allows people to send emails from different devices without compatibility issues.
Disadvantages of SMTP Protocol
1. Spam and Junk Email Risks
- Spammers can misuse SMTP servers to send bulk unwanted emails.
- Open SMTP relays (servers that accept emails from anyone) can be abused for spam, causing problems for users.
2. Security Risks Without Authentication
- SMTP does not have built-in security features to verify users.
- Without proper security measures (like SMTP Authentication), unauthorized people can send fake or harmful emails.
- This can lead to phishing attacks and scams.
3. Emails Can Be Delayed
- If the SMTP server is overloaded or has technical issues, emails may take longer to be delivered.
- Sometimes, emails are stuck in queues, which can be frustrating when sending urgent messages.
4. No End-to-End Encryption by Default
- SMTP does not provide encryption on its own.
- This means emails can be intercepted and read by hackers if not secured with extra layers like SSL/TLS.
5. Not Designed for Receiving Emails
- SMTP is only used for sending emails, not receiving them.
- To receive emails, other protocols like POP3 or IMAP are needed.
Conclusion
The SMTP Protocol is the backbone of email communication, enabling users to send emails securely and efficiently. With the implementation of SMTP Protocol Auth and other security measures, businesses can ensure reliable email delivery. Understanding Mail Protocol SMTP and its role in email transactions helps organizations optimize their email infrastructure.
By leveraging the right Protocol for SMTP, email communication can remain efficient, secure, and scalable for personal and professional use.




